A mass spectrometer determines the mass of a molecule by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio mz of its ion. The abbreviation mz is used to denote the dimensionless quantity formed by dividing the mass number of an ion by its charge number.

Why Does 2 Chloropropane S Mass Spectrum Have A Peak At 27 Chemistry Stack Exchange
M stands for mass and Z stands for charge number of ions.
What does m z mean in mass spectrometry. For example if an ion had a mass of 28 and a charge of 1 its masscharge ratio would be 28. Resolution mass spectrometry In a mass spectrum the observed mz value divided by the smallest difference Δ mz for two ions that can be separated. Mz represents mass divided by charge number and the horizontal axis in a mass spectrum is expressed in units of mz.
If two electrons are removed double charged ions are produced. When calculating the theoretical mz remember to include the charge carriers eg. Once formed ions are electrostatically directed into a mass analyzer where they are separated according to mz and finally detected.
The units for mz are usually not included. Increased charge yields a decreased mz ratio. Add or remove hydrogen atoms and adjust the charge accordingly to simulate gain or loss of protons and to use a positive value or negative value for the charge.
Mass spectrometry is an analytical tool useful for measuring the mass-to-charge ratio mz of one or more molecules present in a sample. Mass resolving poweris defined separately as mΔm in a manner similar to that given above for mass resolution 6. In mass spectrometry the ratio of an ions mass m in atomic mass units to its formal charge z.
An ion with a mass of 56 and a charge of 2 would also have a masscharge ratio of 28. These measurements can often be used to calculate the exact molecular weight of the sample components as well. The number of electrons removed is the charge number for positive ions.
From the mass-to-charges mz we can calculate the molecular masses present The Mass Spectrum Mass spectrometers measure the relative mass-to-charges mz and relative abundances of. Signal intensity of a mass spectrometry peak corresponds to the relative quantity of ions at a given mass-to-charge ratio mz. It has long been called the mass-to-charge ratio although m is not the ionic mass nor is z a multiple or the elementary electronic charge e.
More correctly The mz ratio of H is 1 or H has a mass of 1 Da or The ion H is seen at mz 1 The standard. Formal charge is usually 1. People also ask what does mass spec tell.
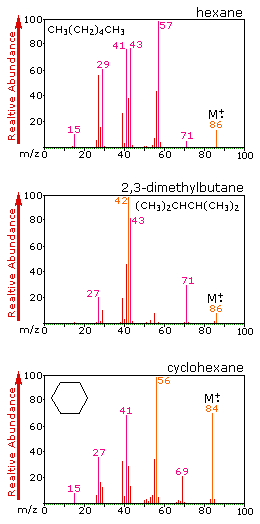
The abbreviation mzis used to denote the dimensionless quantity formed by dividing the mass numberof an ion by its charge number. Two peaks at mz values 43 and 57 will appear in the mass spectrum. Resolving power in mass spectrometryis defined as the ability of an instrument or meas-urement procedure to distinguish between two peaks at mz values differing by a small amount and expressed as the peak width in mass units 6.
Mass spectrometers measure the relative mass-to-charges mz and relative abundances producing a mass spectrum. Fragmentation Ethers di-sec-butyl ether O MW 130 M 130 115 M-15 101 M-29 O H CH3CH2 O H H3C mz 59 mz 45 O H H H3C O H H CH3CH2 mz 57. Typically mass spectrometers can be used to identify unknown compounds via molecular weight.
Mz 57 mz 43 MOLECULAR ION has mz 100 Breaking the bond between the butyl group and the carbonyl group produces two further ions depending on how the bond breaks. Ions are generated by inducing either the loss or gain of a charge from a neutral species. The mass-to-charge ratio mz read m over z is dimensionless by definition.
If two electrons are removed double charged ions are produced. Masscharge ratio is given the symbol mz or sometimes me. 1 mass spectrum many mass spectra.
C What does mz mean. The mz value at which the measurement was made should be reported. Because the largest mz value is 72 that represents the largest ion going through the mass spectrometer - and you can reasonably assume that this is the molecular ion.
Mz as in For H mz 1 Da This represents continued obfuscation of the difference between the unit mz the noun mz ratio and the adjective sym-bol mz. BASIC MASS SPECTROMETRY M stands for mass and Z stands for charge number of ions. Therefore an increase in the number of multiply charged particles increases signal intensity at lower mz ratios.
In mass analysis an electron is taken from molecules to create single charged ions. It has long been called the mass-to-charge ratioalthough m is not the ionic mass nor is z a multiple or the elementary electronic charge e. The relative formula mass of the compound is therefore 72.
The definition and method of measurement of Δ mz should be reported. It is best understood as calculated from the dimensionless mass number m of a given ion and the number of its elementary charges z. In mass analysis an electron is taken from molecules to create single charged ions.
The number of electrons removed is the charge number for positive ions.
12 3 Interpreting Mass Spectra Chemistry Libretexts

Tandem Mass Spectrometry An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
12 3 Interpreting Mass Spectra Chemistry Libretexts